USEFUL LINKS
Australian Organisations
Australian Bureau of Statistics
Australian Government – Department of Agriculture, Water and the Environment – biosecurity
Australian Government – Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade
Australian Government – Department of Industry, Science, Energy and Resources
Australian Tax Office – GST information
Australian Trade and Investment Commission – Austrade
Chamber of Commerce and Industry Queensland
Free Trade Agreements – Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade
International Forwarders & Customs Brokers Association of Australia
Port of Brisbane – Shipping Schedule
Port of Townsville – Live Shipping Schedule
Townsville Chamber of Commerce
Verified Gross Mass Information – Australian Maritime Safety Authority
Global Organisations
Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation
International Air Transport Association
International Chamber of Commerce
Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD)
DOWNLOAD FORMS
General
NQCS Terms and Conditions of Trade
Shipping Container Specifications
Exports
Shippers Letter of Instruction
Imports
Accounts
Border Force Forms
Letter of Authority – Broker Appointment
Unaccompanied Personal Effects Statement
Biosecurity Forms
Acceptable Documentation Templates
These include a variety of acceptable documentation templates, e.g., combined FCL/LCL packing declarations, cleanliness declarations, fumigation certificates, heat treatment certificates, kiln drying certificate, gamma irradiation treatment certificate, and an approved permanent preservative treatment certificate template.
This leads you to the suite of forms relevant to importing and exporting.
International trade terms
The INCOTERM rules are an internationally recognised standard and are used around the world in international and domestic contracts for the sale of goods.
INCOTERM rules provide definitions and rules of interpretation for most common commercial terms. They are accepted by governments, legal authorities, and practitioners worldwide. Put simply, they are the selling terms that the buyer and seller of goods both agree to.
Published by the International Chamber of Commerce, INCOTERMs are mainly used to divide transaction costs and responsibilities between buyer and seller at the same time reflecting the transportation practices.
Regardless of the INCOTERM rules, the seller must supply the goods as agreed in the contract of sale, together with such evidence of conformity as may be required by the contract. The buyer must take receipt and pay for the goods delivered, as provided in the contract.
When a seller and buyer wish to cite Incoterms as applying to the contract of sale, it is important to cite the term used, title and date applicable as there have been numerous amendments over the years.
This overview is provided as a guide only. If you need to know more about Incoterms you should visit the International Chamber of Commerce website.
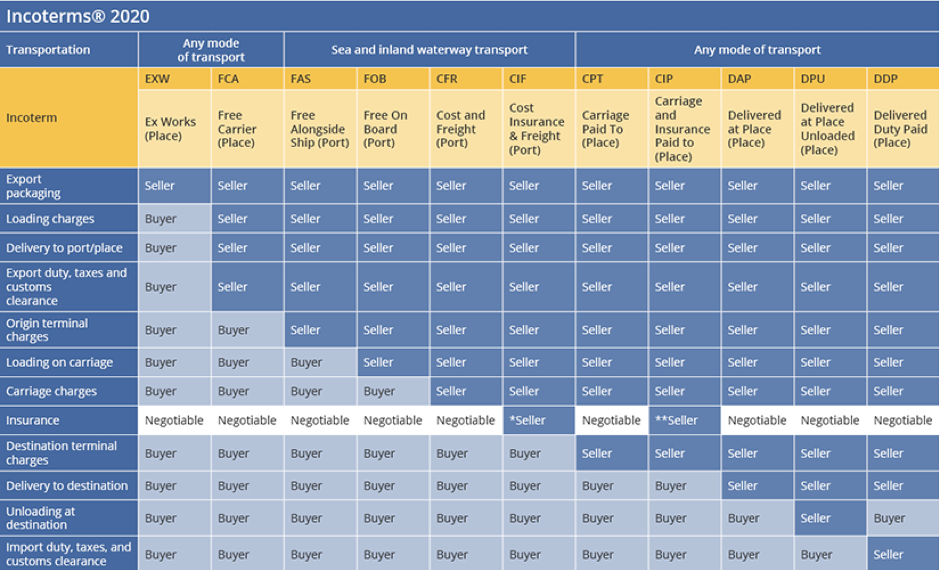
Classifying the Incoterms 2020 rules
Each INCOTERM refers to a type of agreement for the purchase and shipping of goods internationally. There are 11 different terms, each of which helps users deal with different situations involving the movement of goods. The 11 INCOTERMs 2020 rules are presented in two distinct classes:
Rules for any mode of transport
Incoterm | Description |
EXW | ‘Ex Works’ means that the seller delivers when it places the goods at the disposal of the buyer at the seller’s premises or at another named place (i.e., works, factory, warehouse, etc.). The seller does not need to load the goods on any collecting vehicle, nor does it need to clear the goods for export, where such clearance is applicable. |
FCA | ‘Free Carrier’ means that the seller delivers the goods to the carrier or another person nominated by the buyer at the seller’s premises or another named place. The parties are well advised to specify as clearly as possible the point within the named place of delivery, as the risk passes to the buyer at that point. |
CPT | ‘Carriage Paid To’ means that the seller delivers the goods to the carrier or another person nominated by the seller at an agreed place (if any such place is agreed between parties) and that the seller must contract for and pay the costs of carriage necessary to bring the goods to the named place of destination. |
CIP | ‘Carriage and Insurance Paid to’ means that the seller delivers the goods to the carrier or another person nominated by the seller at an agreed place (if any such place is agreed between parties) and that the seller must contract for and pay the costs of carriage necessary to bring the goods to the named place of destination. The seller also contracts for insurance cover against the buyer’s risk of loss of or damage to the goods during the carriage. The buyer should note that under CIP the seller is required to obtain insurance only on minimum cover. Should the buyer wish to have more insurance protection, it will need either to agree as much expressly with the seller or to make its own extra insurance arrangements. |
DAP | ‘Delivered at Place’ means that the seller delivers when the goods are placed at the disposal of the buyer on the arriving means of transport ready for unloading at the named place of destination. The seller bears all risks involved in bringing the goods to the named place. |
DPU | ‘Delivered At Place Unloaded’ means that the seller delivers when the goods, once unloaded, are placed at the disposal of the buyer at a named place of destination. The seller bears all risks involved in bringing the goods to and unloading them at the named place of destination. |
DDP | ‘Delivered Duty Paid’ means that the seller delivers the goods when the goods are placed at the disposal of the buyer, cleared for import on the arriving means of transport ready for unloading at the named place of destination. The seller bears all the costs and risks involved in bringing the goods to the place of destination and has an obligation to clear the goods not only for export but also for import, to pay any duty for both export and import and to carry out all customs formalities. |
Rules for sea and inland waterway transport
Incoterm | Description |
FAS | ‘Free Alongside Ship’ means that the seller delivers when the goods are placed alongside the vessel (e.g., on a quay or a barge) nominated by the buyer at the named port of shipment. The risk of loss of or damage to the goods passes when the goods are alongside the ship, and the buyer bears all costs from that moment onwards. |
FOB | ‘Free On Board’ means that the seller delivers the goods on board the vessel nominated by the buyer at the named port of shipment or procures the goods already so delivered. The risk of loss of or damage to the goods passes when the goods are on board the vessel, and the buyer bears all costs from that moment onwards. |
CFR | ‘Cost and Freight’ means that the seller delivers the goods on board the vessel or procures the goods already so delivered. The risk of loss of or damage to the goods passes when the goods are on board the vessel. The seller must contract for and pay the costs and freight necessary to bring the goods to the named port of destination. |
CIF | ‘Cost, Insurance and Freight’ means that the seller delivers the goods on board the vessel or procures the goods already so delivered. The risk of loss of or damage to the goods passes when the goods are on board the vessel. The seller must contract for and pay the costs and freight necessary to bring the goods to the named port of destination. The seller also contracts for insurance cover against the buyer’s risk of loss of or damage to the goods during the carriage. The buyer should note that under CIF the seller is required to obtain insurance only on minimum cover. Should the buyer wish to have more insurance protection, it will need either to agree as much expressly with the seller or to make its own extra insurance arrangements. |
